the ground – accurately, safely, and without excavation
Geodarar – GPR (Ground Penetrating Radar)
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is an advanced geophysical technology for non-invasive subsurface exploration. It works on the principle of electromagnetic waves that propagate into the ground and reflect the condition of various materials and structures.
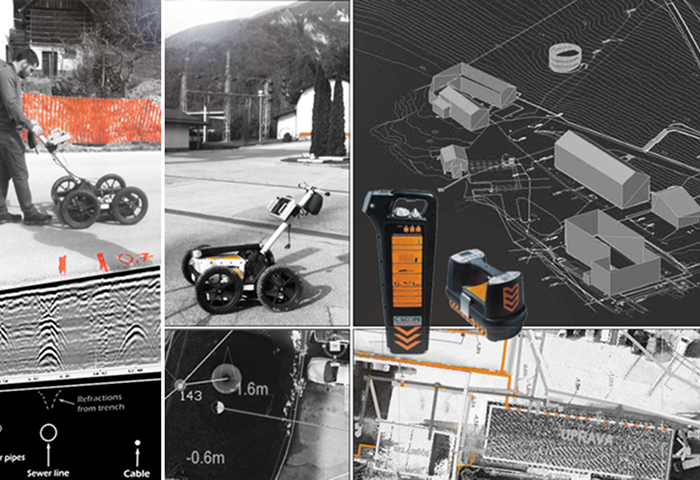

Georadar method or Ultrasonic measurement of underground communications
This method enables the detection and mapping of underground infrastructure, structures, cavities, geological layers, and other anomalies without excavation or damage to the terrain. Due to its high accuracy and fast data capture, GPR is an indispensable tool in construction, geodesy, archaeology, municipal infrastructure management, and security risk assessment.
Geodadar reach depth
The location and depth accuracy of GPR measurements depends on the soil composition and antenna selection. High-frequency antennas (1000 MHz) provide better data resolution but less depth penetration (< 1 m). To achieve greater depths, we use low-frequency antennas, which reduce resolution but allow us to detect greater changes in the subsurface. The depth of georadar measurements can thus reach up to 10 m.
Geodadar reach depth
The location and depth accuracy of GPR measurements depends on the soil composition and antenna selection. High-frequency antennas (1000 MHz) provide better data resolution but less depth penetration (< 1 m). To achieve greater depths, we use low-frequency antennas, which reduce resolution but allow us to detect greater changes in the subsurface. The depth of georadar measurements can thus reach up to 10 m.
Areas of application of GPR:
- Construction and engineering – detection of underground installations, foundation inspection, and structural condition monitoring.
- Municipal infrastructure – locating water, sewer, and other networks without excavation.
- Geology and environment – studying geological layers, groundwater, cavities, and landslide areas.
- Archaeology and cultural heritage – detecting archaeological structures without damaging the terrain.
- Transport and infrastructure – analysis of roads, railways, and airport surfaces and detection of degradation layers.
- Security and forensics – searching for buried objects, weapons, and unexploded ordnance.

Latest projects